Automotive Flooring
Polyurethane (PU) foam is a versatile material widely used in automotive flooring to enhance comfort, insulation, and noise reduction. Its lightweight, durable, and flexible properties make it ideal for creating a quieter, more comfortable cabin environment while contributing to overall vehicle performance.
Key Applications of PU Foam in Automotive Flooring
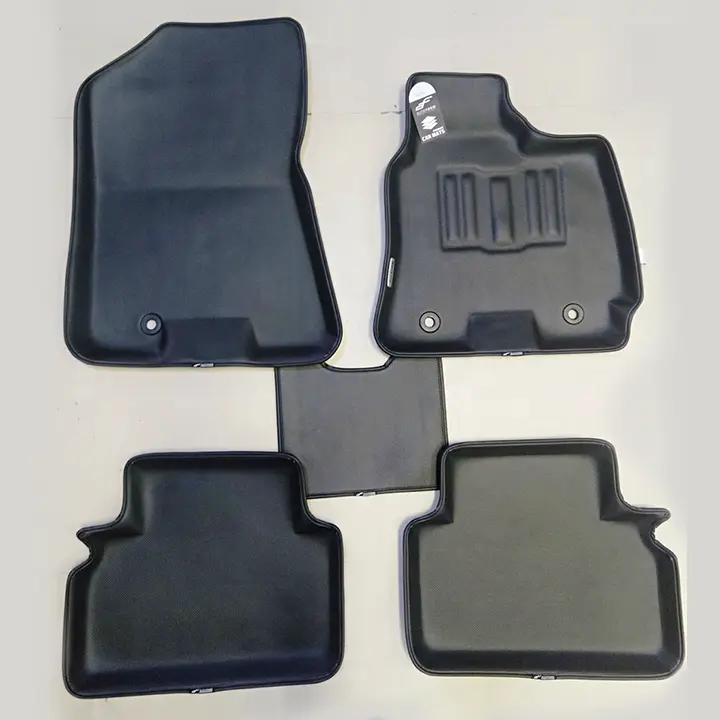
Under-Carpet Padding: PU foam acts as a cushioning layer beneath carpets, improving seating comfort and ergonomics while providing a soft, supportive feel underfoot.
Sound Deadening Layer: Open-cell and flexible PU foams help reduce road noise, engine vibrations, and structural rattles, effectively addressing NVH (Noise, Vibration, Harshness) concerns in passenger cabins.
Thermal Insulation: PU foam provides a barrier against heat transfer from the engine bay, exhaust system, or external environment, helping maintain a comfortable cabin temperature and improving HVAC efficiency.
Description
Floor Panel Insulation: PU foam fills cavities in vehicle floor structures, minimizing rattling, vibrations, and sound transmission, which contributes to a quieter and more refined ride experience.
Molded Foam Flooring Inserts: For complex floor geometries—particularly in electric vehicles (EVs) or premium models—PU foam can be precisely molded to fit, ensuring consistent insulation, comfort, and structural support.
Polyurethane foam’s combination of comfort, sound absorption, thermal insulation, and adaptability makes it an essential material in modern automotive flooring solutions, enhancing passenger experience while supporting vehicle design and performance requirements.
Common PU Foam Types Used:
| Type | Key Features | Usage |
| Flexible PU Foam | Soft, resilient | Carpet underlay |
| Semi-rigid Foam | Structural and insulative | Molded inserts, panel linings |
| Open-cell PU Foam | Excellent sound absorption | NVH treatment under floors |
Applications of Polyurethane Foam in Automotive Flooring:
Under-Carpet Padding: Acts as a cushioning layer beneath carpets to improve comfort and ergonomics.
Sound Deadening Layer: Helps reduce road noise and vibrations (NVH – noise, vibration, harshness).
Thermal Insulation: Provides a barrier against heat transfer from the engine bay or exhaust system.
Floor Panel Insulation: Fills cavities in floor structures to reduce rattling and insulate against heat and sound.
Molded Foam Flooring Inserts: PU foam is shaped to fit complex vehicle floor geometries, especially in EVs or premium models.
Benefits of PU Foam in Flooring:
Lightweight: Contributes to overall vehicle weight reduction.
Flexible Design: Moldable to fit contours of the cabin floor.
Durability: Resists compression and wear from prolonged foot traffic.
Multi-functionality: Provides both thermal and acoustic insulation in one material.
Compatibility: Bonds well with other flooring materials like carpets or liners.
Manufacturing Techniques:
Molded Foam Underlay: PU is poured into molds to match floor contours.
Laminated Foam Layers: PU foam is bonded to carpets or non-woven fabric for easy installation.
Spray Foam or Pour-in-Place: Used in structural cavities for insulation and bonding.