Global Flexible Foam Production: Engineering Comfort on a Global Scale
Flexible Polyurethane (PU) foam is one of the most versatile synthetic materials ever engineered. As of late 2025, the global market for flexible foam has reached a valuation of approximately $56.8 billion, with projections to climb to $75.2 billion by 2029. This growth is underpinned by a 7.3% CAGR, driven by a dual demand for lightweight electric vehicle (EV) interiors and high-performance ergonomic bedding.
At Foam Villa, we recognize that flexible foam is not just a commodity; it is a critical functional material that dictates the user experience in everything from automotive seating to medical positioning pads.
The Global Market Landscape: Regional Powerhouses
While North America and Europe remain hubs for specialty foams and sustainable innovation, the center of gravity for production continues to shift East.
Asia-Pacific Dominance: This region currently holds a massive 46% share of the global market. Driven by the automotive hubs and urbanization in China and India, APAC is not only the largest producer but also the fastest-growing market, expanding at nearly 7.8% annually.
The Sustainability Mandate in Europe: European manufacturers are leading the “Circular Economy” shift. Innovations like CO2-based polyols and chemical recycling—breaking down old PU into its original liquid components—are now becoming the industry standard to meet 2030 “Net Zero” targets.
North American Innovation: Focus has shifted toward “Bed-in-a-Box” logistics and advanced healthcare foams, with a strong emphasis on reducing VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) emissions.
The Chemistry of Flexibility: Advanced Raw Materials
The “feel” and “durability” of flexible foam are determined long before the foam rises. It is a precise chemical orchestration:
Bio-Based Polyols: In 2025, there is a significant surge in renewable polyols derived from vegetable oils and lignocellulosic biomass. These are the fastest-growing feedstock segment, logging a 6.9% CAGR as industries move away from petroleum.
Next-Gen Blowing Agents: To meet environmental regulations like the Kigali Amendment, the industry has transitioned to HFOs (Hydrofluoroolefins) and water-based CO2 systems, which have zero Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) and ultra-low global warming potential.
The Strategic Role of Precision Foam Components Across Global Industries
 In the modern industrial ecosystem, success is built on the reliability of small, often invisible parts. Precision foam components, fabricated from a wide range of polyurethane (PU) formulations, have become essential assets in enhancing product comfort, structural protection, and operational efficiency. By transforming raw polymers into engineered components, we are supporting diverse sectors—from high-performance aerospace modules to life-saving medical devices.
In the modern industrial ecosystem, success is built on the reliability of small, often invisible parts. Precision foam components, fabricated from a wide range of polyurethane (PU) formulations, have become essential assets in enhancing product comfort, structural protection, and operational efficiency. By transforming raw polymers into engineered components, we are supporting diverse sectors—from high-performance aerospace modules to life-saving medical devices.
The Architecture of a Component: Precision and Function
A foam component is far more than a simple cutout; it is a meticulously engineered part designed to solve specific physical challenges. Utilizing world-class conversion technology, these components are fabricated to maintain consistent thickness and exact tolerances. This precision allows for seamless integration into high-speed assembly lines, effectively streamlining the manufacturing process while significantly elevating the quality of the final product.
Industry-Specific Integration
The versatility of PU foam components allows them to serve as a sophisticated “multi-tool” across diverse sectors:
Automotive Engineering: Foam components are vital for NVH (Noise, Vibration, and Harshness) management. Custom-fabricated seals and gaskets within dashboards, door panels, and HVAC systems ensure cabin quietness and thermal regulation.
Electronics & Semiconductors: In the world of micro-technology, foam components act as thermal gap fillers and shock absorbers, safeguarding delicate circuitries from the twin threats of heat and kinetic energy.
Medical & Healthcare: Beyond simple padding, medical-grade components are used for equipment cushioning and sterile packaging inserts, ensuring the integrity of high-value diagnostic tools.
Building Science & Construction: High-density foam components provide the airtight and watertight seals necessary for energy-efficient windows, roofing systems, and industrial HVAC units.
Aerospace & Defense: Lightweight but durable, these components assist in weight reduction while providing critical vibration damping for sensitive cockpit instrumentation.

The Multi-Material Advantage: Chemistry and Customization
A key part of our “Foam Knowledge” is selecting the specific chemical family for the task. Whether utilizing Polyether for its hydrolytic stability and moisture resistance or Polyester for its superior chemical and oil resistance, each material choice is intentional. For higher impact protection, Polyethylene and specialized Moulded Foams offer high-density structural integrity.
To meet specific industrial demands, these components are available with secondary processing options. This includes pressure-sensitive adhesive backings for rapid installation, specialized surface coatings for environmental protection, and multi-layer lamination to combine different foam properties into a single, high-performance part.
Key Functional Missions
The “Material Intelligence” of an engineered foam component is defined by its primary role in an assembly. For instance, in Environmental Sealing, the foam creates an impermeable barrier against dust and moisture. In Acoustic Management, the cellular structure is tuned to absorb specific sound frequencies. For Specialized Packaging, the focus shifts to 360-degree contouring, offering total protection for fragile goods during global transit.
The Evolution of Support: Why the Architecture of Your Mattress Dictates Longevity
On average, a human being will spend nearly approximately one-third of their life—resting on a mattress. Over a single year, an adult accumulates upwards of 3,200 hours of contact time with this single surface. From a technical perspective, the mattress is the most frequently used “equipment” in a household, making its material composition the primary factor in long-term musculoskeletal health.
The Origin of the Mattress: From Necessity to Engineering
The concept of the mattress was born from the basic human need to insulate the body from the cold, hard ground. Early iterations were rudimentary—bags of straw, wool, or horsehair designed for thermal protection rather than orthopedic support.
The true revolution occurred during the industrial era with the introduction of steel coils, but it was the mid-20th-century development of Polyurethane and Memory Foams that changed everything. This shift allowed for “Contouring Support,” where the material finally began to adapt to the human shape, rather than forcing the human body to adapt to the surface. Today, we view the mattress not as a bag of filler, but as a sophisticated multi-layered system designed to manage gravity.
The Mechanics of Orthopedic Integrity
A high-performance mattress must solve two conflicting physical problems: it must be soft enough to relieve pressure but firm enough to maintain spinal neutrality.
When a surface fails to provide Pressure Relief, blood flow is restricted to the skin and soft tissues, triggering the brain to command the body to move. This “tossing and turning” disrupts the deep sleep cycles necessary for cognitive repair. Simultaneously, Spinal Alignment is critical; if the mattress allows the hips to sink too deeply, the lumbar spine is placed under constant tension, leading to the chronic back pain that plagues many modern professionals.
Individualized Requirements: Weight, Age, and Physiology
There is no “universal” mattress because human anatomy varies significantly across different demographics. The effectiveness of a support system is largely determined by the “load” placed upon it.
- Weight Dynamics: Heavier individuals require higher-density foam cores and higher ILD (Indentation Load Deflection) ratings to prevent “bottoming out.” Conversely, lighter individuals may find high-density foam too rigid, as they lack the body mass to engage the foam’s contouring properties.
- The Aging Factor: As we age, skin becomes thinner and joints more sensitive. For seniors, the priority shifts toward high-compliance materials like Latex or Memory Foam that minimize surface tension.
- Health Considerations: For those with chronic respiratory issues or allergies, hypoallergenic materials such as closed-cell foams or treated latex are essential for maintaining air quality during the 8-hour sleep window.
Restorative Logic: Why Sleep is the Ultimate Productivity Tool
In our modern, high-pressure landscape, sleep has evolved from a simple rest period into a critical biological defense mechanism. As our daily lives become increasingly dominated by digital interfaces, sedentary work, and intense professional expectations, the physiological “cost” of being awake has reached an all-time high.
The Digital Toll and Cognitive Fatigue
The shift toward prolonged mobile phone and screen usage has introduced a profound disruption to human biology. The blue light emitted by these devices—specifically within the 450–495 nm range—tricks the brain into suppressing melatonin, the hormone responsible for the onset of sleep. Beyond the chemical impact, the “infinite scroll” of digital content keeps the mind in a state of high arousal. This prevents the mental relaxation required to enter restorative deep sleep, leaving the mind cluttered and leading to a state of chronic burnout.

Physical Burden: Posture and the Modern Lifestyle
Current work-life scenarios have significantly worsened musculoskeletal health. Many professionals spend the majority of their day in a state of physical compression—whether sitting at a desk for eight hours or navigating long, stressful commutes. These activities place immense strain on the spinal discs and cervical muscles. Sleep is the only period during the day when the spine can truly decompress. If this window of rest is neglected, or if the support surface is inadequate, the physical strain of the day is “carried over,” manifesting as chronic pain and long-term spinal degradation.
The Biological Requirement Across the Lifespan
While the general recommendation for adults is seven to nine hours of rest, sleep requirements are actually a moving target that shifts with the body’s developmental stages. Infants and children require significantly more time for rapid physical growth and immune priming, while teenagers need extended rest to facilitate hormonal balancing. For the working adult, seven to eight hours is the non-negotiable threshold for tissue repair and metabolic health.
| Age Group | Recommended Duration | Primary Biological Function |
| Infants & Toddlers | 12 – 16 Hours | Rapid growth and brain development |
| School Age & Teens | 9 – 12 Hours | Cognitive loading and emotional regulation |
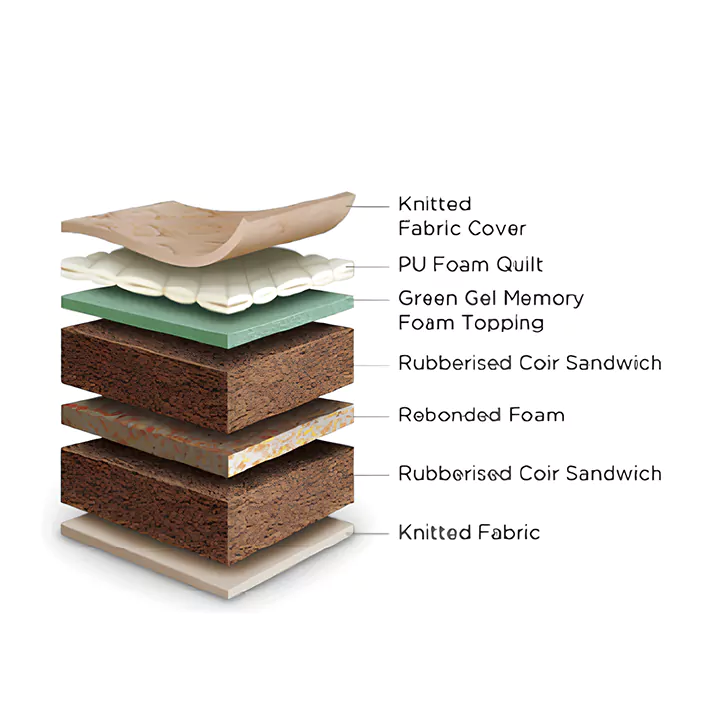
Rebonded Foam: Engineering Circularity and High-Density Support
In the modern manufacturing landscape, the transition from a linear “take-make-waste” model to a circular economy is no longer optional. Rebonded foam stands at the forefront of this shift. Far from being a mere byproduct, rebonded foam is a sophisticated, high-density engineered material created through the precise recycling of polyurethane scraps. It represents the perfect intersection of environmental stewardship and industrial-grade performance.
The Mechanics of the Rebonding Process
The transformation of loose foam scrap into a structural block is a feat of mechanical engineering. Unlike virgin foam, which relies on a chemical reaction to rise, rebonded foam is “constructed.”
Precision Shredding & Pulverization: Advanced technology now allows manufacturers to crush foam into nearly powder-like particles. This reduction in “chip size” is critical; the smaller the particle, the more uniform the final block’s cellular structure.
Polymer Bonding: These particles are coated with high-performance prepolymer bonding agents. The quality of this adhesive determines the foam’s “tear strength” and long-term resilience.
Thermo-Compression: The mixture is subjected to intense hydraulic pressure and steam injection. This is where density is dictated. While standard grades range from 60 to 110 kg/m³, latest-generation technology can compress these particles into ultra-high-density grades reaching 220 kg/m³. At this level, the foam becomes almost as rigid as wood but retains the vibration-dampening properties of a polymer.
Why Density Dictates Application
The versatility of rebonded foam is a direct result of its customizable density. Because the “mass per unit volume” can be controlled during the pressing stage, it can be tailored to specific industrial needs:
Orthopedic Foundation (80–120 kg/m³): In the bedding industry, rebonded foam serves as the “core” or base layer. It provides a non-sagging foundation that supports the heavier areas of the human body, ensuring the softer comfort layers above it perform optimally.
Acoustic & Vibration Control (120–180 kg/m³): Due to its high mass and irregular internal structure (created by the various foam chips), rebonded foam is an exceptional sound absorber. It is widely used in automotive floorings and generator room insulation to dampen low-frequency vibrations.
Industrial Impact Protection (200+ kg/m³): The highest grades are utilized in sports flooring, heavy-duty packaging, and gym mats where the material must withstand repetitive, high-impact force without permanent deformation.
Environmental Impact and Market Insights
The global demand for rebonded foam is surging, driven by a “Green Manufacturing” mandate. By consuming foam scrap—which would otherwise contribute to landfill volume—this process cleans the environment while providing a cost-effective alternative to virgin materials.
For the consumer and the industrial buyer, the benefits are clear: rebonded foam offers a higher Support Factor and greater Durability than many standard foam grades, often at a lower price point. It is a rare example of a recycled product outperforming the original in specific high-load applications.
Final Insight
Rebonded foam is not just “recycled foam”; it is a reclaimed asset. Its ability to be engineered to extreme densities (up to 220 kg/m³) makes it a vital component in everything from the mattress you sleep on to the car you drive. At Foam Villa, we view this material as a testament to what “Material Intelligence” can achieve for both the industry and the planet.
Written by the Foam Villa Editorial Lab Specializing in high-performance rebonded solutions and sustainable polymer engineering. We help industries optimize support and minimize waste through advanced foam technology.